Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
Published:
Key Summery
This paper is about ResNet (Residual Network). Resnet is a model that enables efficient learning by using residual connections to solve the gradient loss problem in deep neural networks.
1. Background
Deeplearning
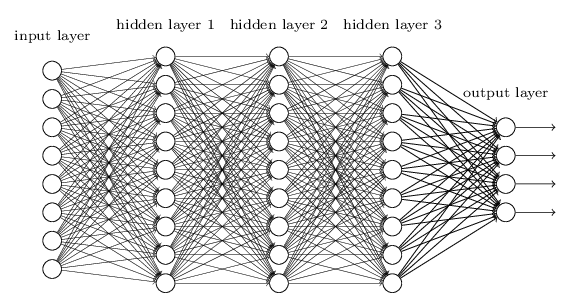
- To understand resnet, need to know what deep learning is. Deep learning is a method of learning data with multiple layers of neural networks, and the structure consists of an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer, like above image.
- Learning is done by informing deep learning of the correct answer and making it follow along, and it goes through the process of correcting the problem by looking backward to reduce errors.
- Through this process, the network adjusts its weight so that it approaches the correct answer more and more accurately.
Residual Learning Framework
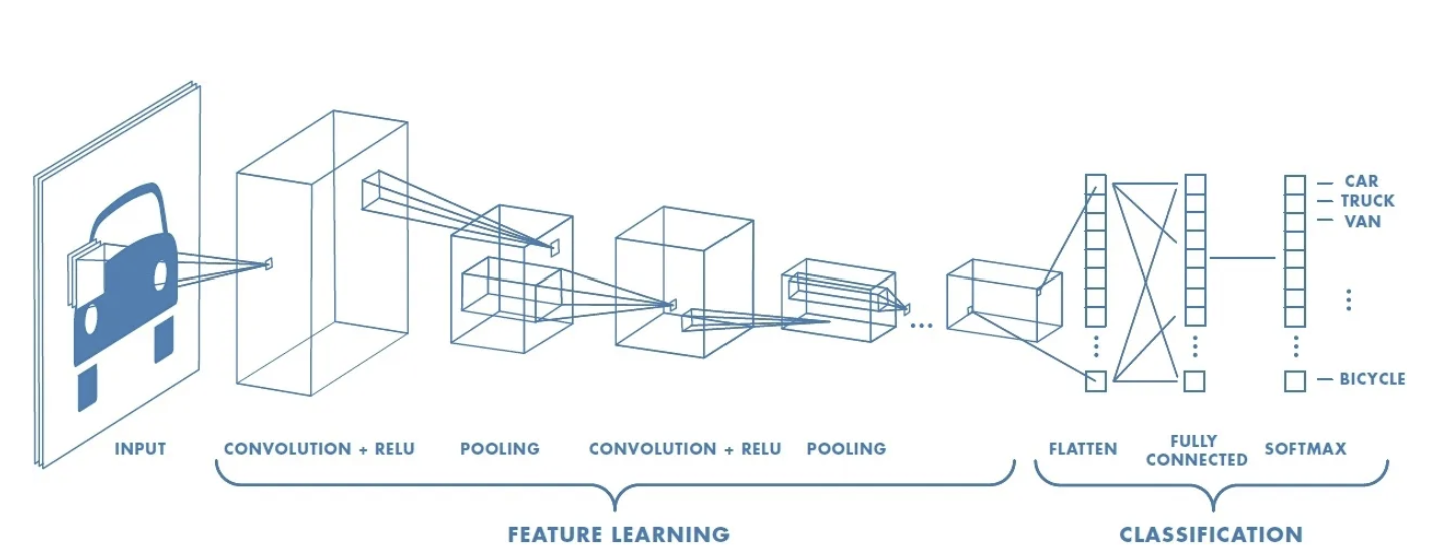
- CNN (Convolutionary Neural Network) is a type of deep learning, an artificial intelligence algorithm that automatically finds important features in an image.
- CNN analyzes small parts of an image like the image, to recognize basic features such as edge or texture, and then learns increasingly complex shapes or patterns through multiple layers.
2. Abstract
Problem
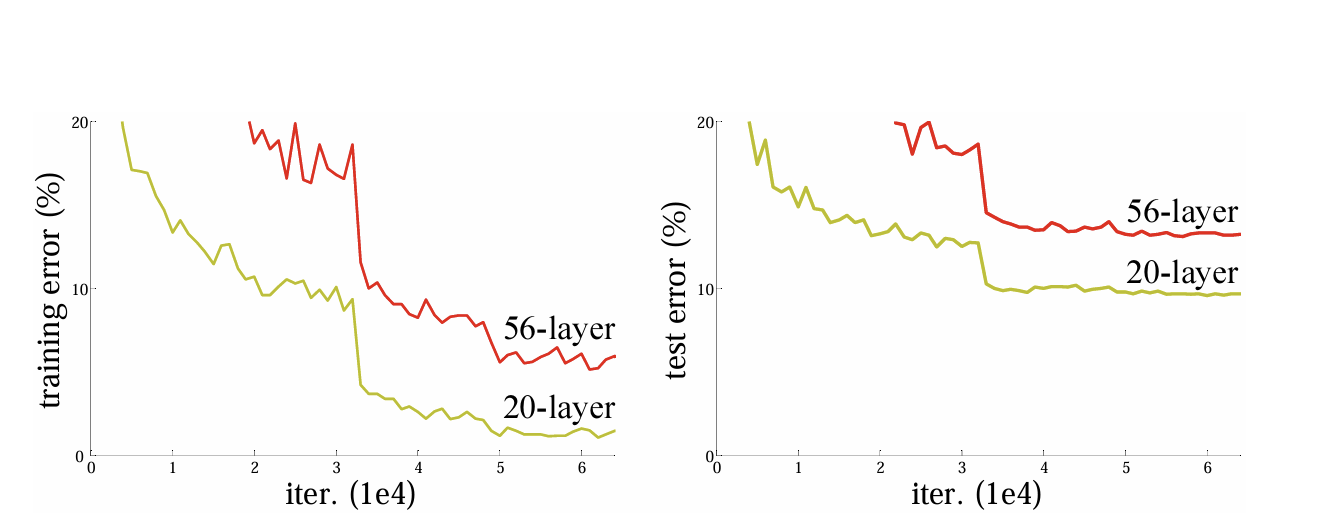
In prior deep learning, especially CNN, the more layers, the more complex patterns can be learned, but as above, training and test error increased when the more layer has.
Several methods have been tried to solve this problem, but degradation problem has occurred when the layers is bigger in a certain depth, which degrades the performance. To solve this problem, Deep Residual Learning(resnet) emerged.
Solution
- Residual Learning (Residual Network, Resnet)
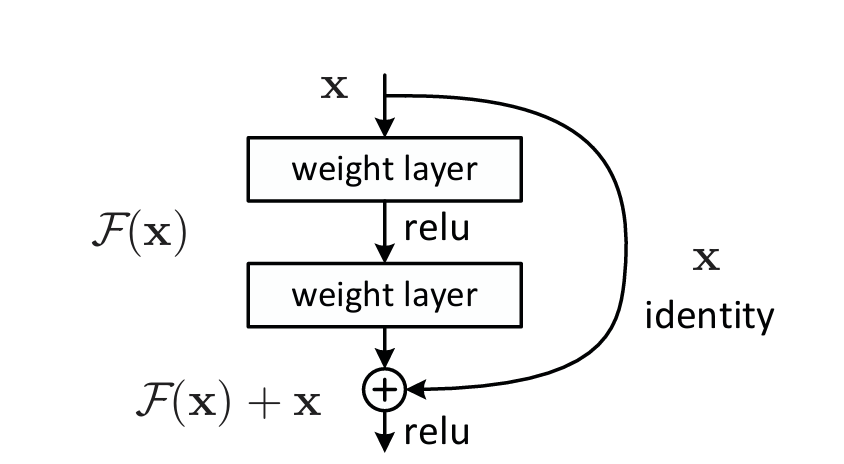
The key idea of ResNet is that each layer is a full mapping function. Instead of learning H(x), let them learn the residual function F(x)=H(x)-x
For example, if each layer learns the difference by referring to the input using the F(x) + x structure, smooth learning is possible even in deeper networks.
This structure was created using “Short-cut Connection”, which enables reliable learning without complex calculations or additional settings.
Experiment & Applicability
First, it records the highest performance with a network of 152 layers of ImageNet.
Second, other datasets such as CIFAR-10 were able to maintain low error rates at depths above 100 layers.
Furthermore, it performs well in visual recognition tasks such as object detection and image segmentation such as COCO,
a variety of utilization with the following results.
“Our 152-layer residual net is the deepest network ever presented on ImageNet, while still having lower complexity than VGG nets” (He, Zhang, Ren, & Sun, 2015).
“1st places on: ImageNet detection, ImageNet localization, COCO detection, and COCO segmentation in ILSVRC & COCO2015 competitions” (He, Zhang, Ren, & Sun, 2015).
3. About Residual Learning
3.1 Residual Learning
Target function: The final target function that we want to calculate is H(x).
Existing method: Originally, we tried to learn H(x) directly, but ResNet lets us learn *residual function : F(x) = H(x)-x.
3.2 Short-cut connection
Shortcut Connection is a key concept that makes resnet.
It refers to a connection method in which the output of a particular layer is skipped across multiple layers and directly transferred to the next layer in a neural network.
This method allows only gap(residue) between input and output to be learned, so, reducing the problem of gradient loss and helping to learn efficiently as the network deepens.
\[y = \mathcal{F}(x, \{W_i\}) + W_s x\]Also, if the input and output dimensions are different, use the Projection 𝑊𝑠 in the Shortcut Connection to fit the dimensions.
3.3 Adventage of resnet by Shorcut Connection
So, what’s good about calculating through resnet?
Ease of optimization: Learning F(x) close to zero makes input and output similar (if F(X) goes 0, it means H(x)=x), making optimization easier without complex transformations by learning small differences only when needed.
Degradation Problem Solved: In the F(x)+x structure, the gradient of 𝑥 is added as 1 during gradient calculation, helping to prevent gradient vanishing.
3.4 Network Architectures
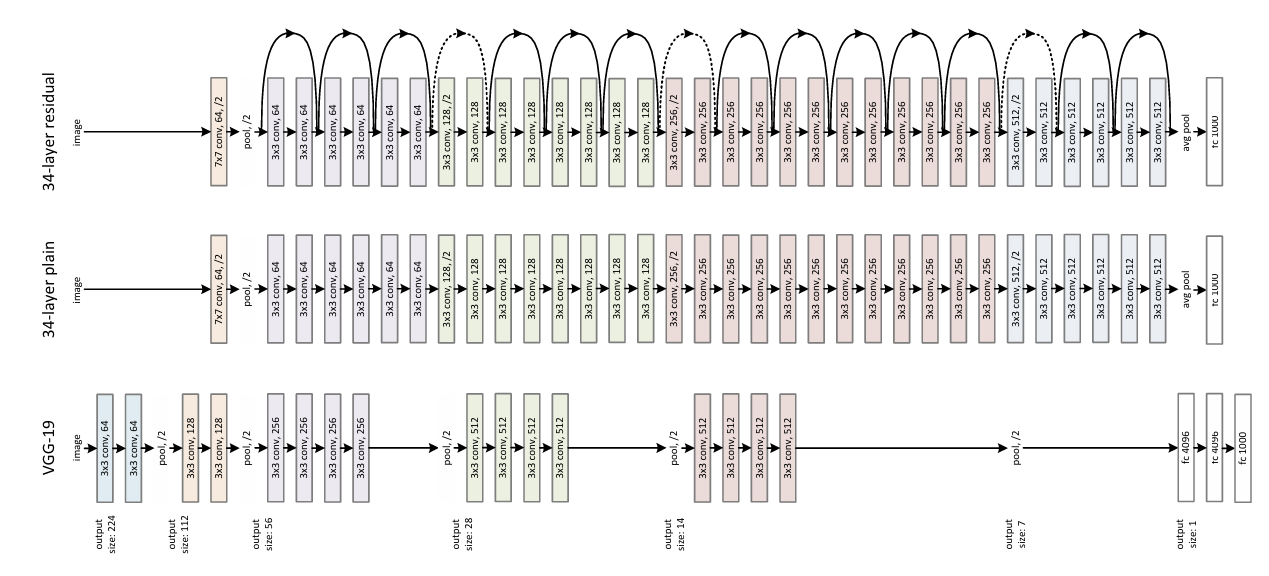
Plain Network: It is a VGG-based neural network.
- Mainly use 3x3 filters, equalize the number of filters when the output size is the same, double the number of filters when the output size is halved, and set the convolutional layer’s stride to 2 when reducing the image
Residual Network: It is a model that adds Shortcut Connection to the Plain Network.
- Connect directly when the input and output sizes are the same, and adjust in two ways when the sizes are different
a. Add 0 to increase the dimension. b. Use 𝑊𝑠 to adjust the dimensions. So, we can understand about difference between plain network and resdiaul network
4. Related work
Residual Representations: Utilizing residuals in image retrieval and classification is more efficient, and multi-grid methods speed up problem solving.
Short connections: ResNet always leaves short connections open to deliver all the information and solves the problem of gradient loss by learning only the residuals.
5. Experiment
The researchers conducted experiments using both the ImageNet and CIFAR-10 datasets, evaluating networks of various depths:
CIFAR-10 dataset
- consisting of 50,000 training images and 10,000 test images, corresponding to 10 classes.
This work focuses on investigating the behavior of very deep networks.
Architecture
- Use 32x32 image input, apply 3x3 convolution to first layer
Results
The residual network recorded a Top-1 error rate of 25.03% at 34 layers, showing better actions than the general network. The residual network tends to have a lower error rate as it gets deeper.
Network navigation over 1,000 layers, experimented with a network of 1,202 layers, which achieved less than 0.1% training error.
Analysis
- The layer response of network showed a lower standard deviation than that of the plain network.
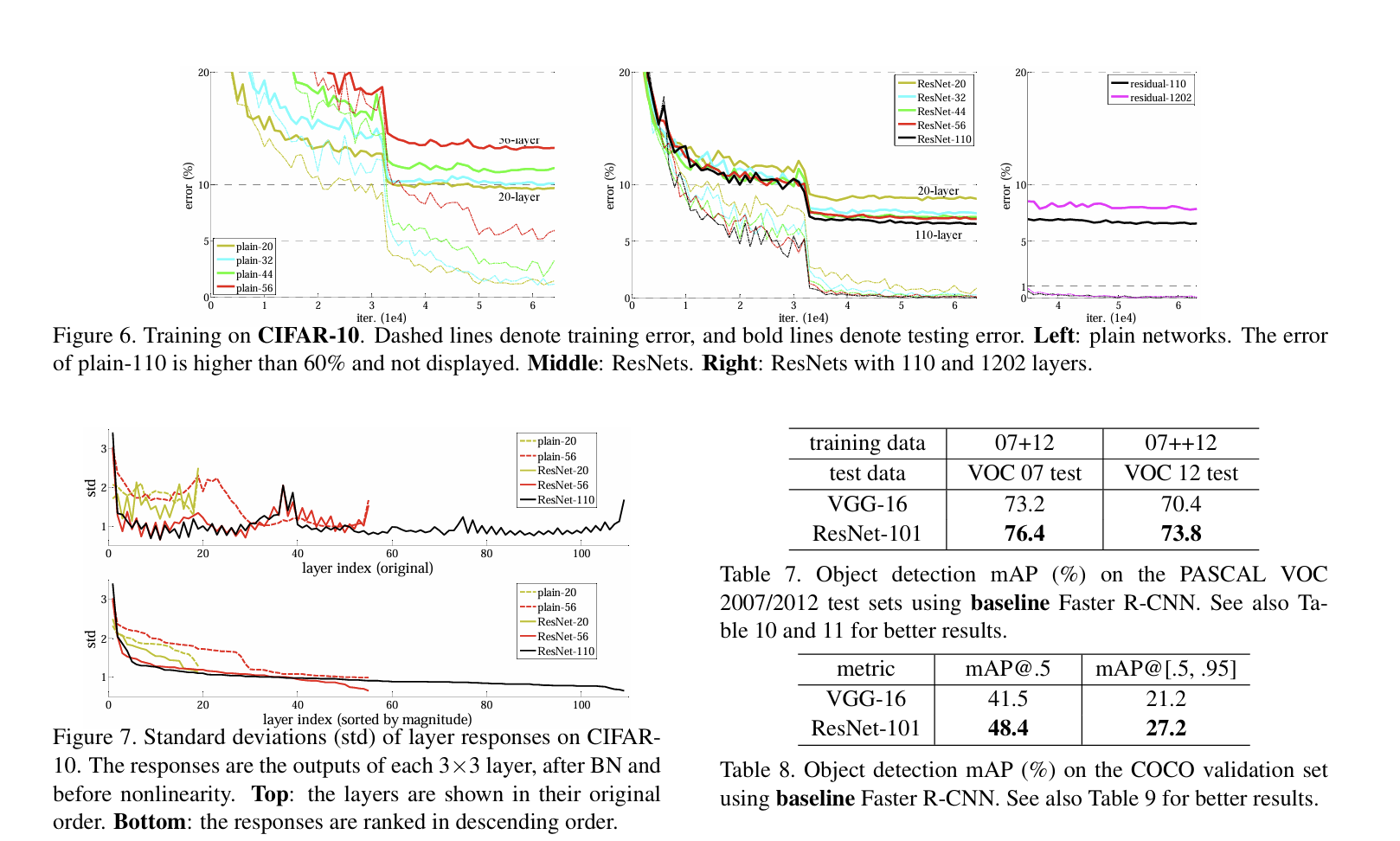
This shows how residual networks handle depth increases much more effectively.
Enhancing Object Detection and Localization Performance Using ResNet
A. Object Detection Baselines The study shows a detection method based on Faster R-CNN, using ResNet-50/101 model. ResNet-101 showed a greater than 3% improvement.
B. Object Detection Improvements The study shows method includes box refinement, global context integration, and enhancement for MS COCO and PASCAL VOC datasets with a 59.0% mAP on the test-dev set for COCO.
C. ImageNet Localization The localization task focused on localizing objects, using a per-class regression strategy. The results show a big reduction in localization error that is first place in the ILSVRC 2015 localization task.
Conclusion
Deep Residual Learning is a new approach that solves the problem of performance degradation of plain networks.
Also, it enables optimization even in deep networks, can maintain the efficiency of learning while increasing the network depth.
The paper suggests that the principle of resnet is useful for general problem solving, and residual learning will also be an important foundation for various visual and vision problems.
Image Reference
Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers, “Deep Learning,” KIISE Website, (accessed November 1, 2024).
Prabhu, Raghav. “Understanding of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) - Deep Learning.” Medium, (accessed November 1, 2024).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015). Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385.
References
- He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015). Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385.
